Describe the Role of Myelin Sheath
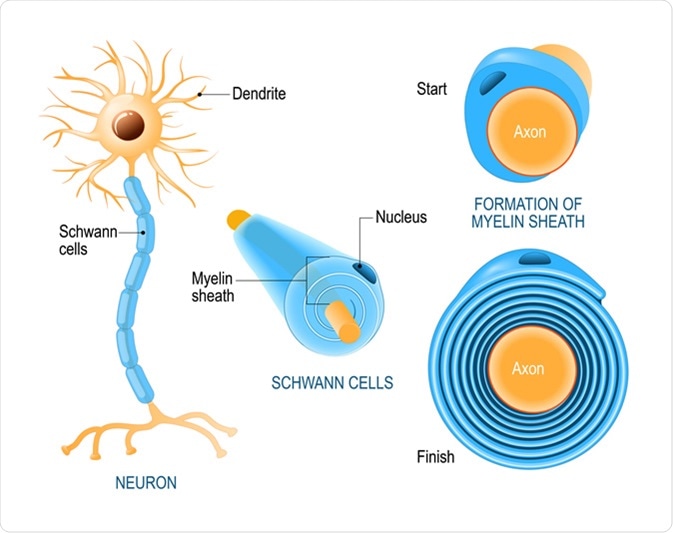
The myelin sheath is a greatly extended and modified plasma membrane wrapped around the nerve axon in a spiral fashion 1. Briefly describe how nerve impulses are transmitted within a neuron including the role of the myelin sheath.
It is made up of protein and fatty substances.

. The sheath protects these fibers known as axons a lot like the insulation around an electrical wire. What Meilin chief is its me the fence and its increases the speed of conduction. Briefly describe how nerve impulses are transmitted within a neuron including the role of the myelin sheath.
One of the biochemical characteristics that. The myelin sheath is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system. 1 It acts as an electrical insulator for the neurone - it prevents electrical impulses travelling through the sheath.
The myelin sheath and myelination. Click again to see term. Tap again to see term.
This myelin sheath allows electrical impulses to transmit quickly and efficiently along the nerve cells. Myelin sheath is the protective layer that wraps around the axons of neurons to aid in insulating the neurons and to increase the number of electrical signals being transferred. What is the function of the myelin sheath.
Click to see full answer. Tap card to see definition. Click card to see definition.
The intertwining hydrocarbon chains of sphingomyelin. The myelin sheath is made out of a modified plasma membrane that is wrapped around the nerve axon in a spiral pattern. Most nerve fibres are surrounded by an insulating fatty sheath called myelin which acts to speed up impulses.
Function is to protect the neuron provide insulation and increase the speed of impulse transmision. If myelin is damaged these impulses slow down. It protects them from any injury or damage.
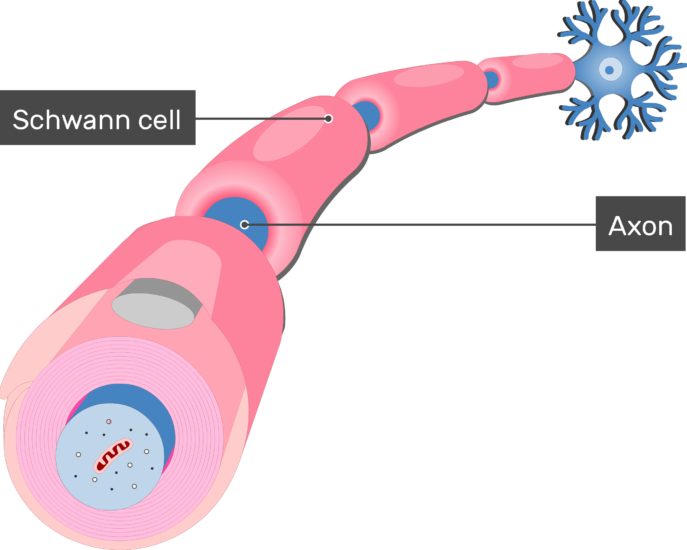
Function of the Myelin Sheath. The myelin sheath is needed to insulate nerves from each other and to speed the time signals pass along long nerves. Peripheral nervous system PNS myelin is formed by the differentiation of the plasma membrane of Schwann cells.
Flat cells that surround cell body 2. Its helps electrical signals move along nerves. Without this functions signals become mixed and normal movements become impossible.
2 The sheath prevents the movement of ions into or out of the neurone it prevents depolarisation. The myelin sheath Schwann cells and nodes of Ranvier are all related to the nervous system and multiple sclerosis MS. Myelin is an insulating layer or sheath that forms around nerves including those in the brain and spinal cord.
This sheath is composed. Myelin sheath is the insulation of the CNS central nervous system. The myelin sheath is a protective covering that surrounds fibers called axons which are the long thin projections that extend from the main body of a nerve cell or neuron.
It preserves the ionic concentration on both sides of the membrane and maintains the electrical potentials. Briefly describe how a neuron transmits a signal from its transmissive segment to its target cell. The primary lipid of myelin is a glycolipid called galactocerebroside.
Myelin sheath also protects the axonal nerve fibres. 3 It speeds up conduction. Briefly describe how nerve impulses are transmitted within a neuron including the role of the myelin sheath.
This allows INSULATION which in turn allows quicker conduction of electrical impulses. Cells that make the myelin sheath. So um when an electrical imports passes along bi axle because we mind the chief is on the axe on Lets say this is the usual speed.
Explore the role of all three in the development of MS and the action. The myelin membranes originate from and are a part of the Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system PNS and the oligodendroglial cells in the central nervous system CNS see Chap. In the PNS myelin protein zero MPZ or P0 has a similar role to that of PLP in the CNS in that it is involved in holding together the multiple concentric layers of glial cell membrane that constitute the myelin sheath.
So for this question were saying What is the function of a mile in chief. Propose physiological symptoms that would most likely accompany the destruction of the myelin sheath in the peripheral nervous system. The function of the myelin sheath is to facilitate the conduction of electrical impulses through the nerve cells.
It is made up of many concentric layers of plasma. It is made up of protein and fatty substances. Myelin is made up of lipids and proteins a fatty substance with a whitish appearance.
Create myelin sheath around PNS axons Satellite cells 1. The myelin sheath contains periodic breaks called nodes of Ranvier. Myelin is an insulating layer or sheath that forms around nerves including those in the brain and spinal cord.
Describe the role of the myelin sheath surrounding the axon It is important to remember that the myelin sheath is essential for our nervous systemIt forms a layers of fatty material around the axon. By jumping from node to node the impulse can travel much more quickly than if it had to travel along the entire length of the nerve fibre. By imposing saltatory conduction on the nervous impulse the principal role of the myelin sheath is to allow the faster propagation of action potentials along the axons which it surrounds.
Electrical Insulation Another important function of myelin is to provide electrical insulation to the nerve fibres. The myelin sheath wraps around the fibers that are the long threadlike part of a nerve cell. Provide structural support 3.
If myelin is damaged these impulses slow down. This myelin sheath allows electrical impulses to transmit quickly and efficiently along the nerve cells. An axon is usually wrapped by the myelin sheath around its whole length in order to increase the speed of these electrical signals allowing all actions to be conducted quickly.
Basically its synonymous with insulated wire. Blindness and other neurological conditions related to nerve damage occur when the myelin sheath is removed. Regulate flow of material between neuron and interstitial fluid Recommended textbook explanations Anatomy Physiology Student Workbook 2nd Edition Kent Pryor Richard Allan Tracey Greenwood 695 explanations.

Myelin Sheath An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Myelin Sheath Definition And Function Biology Dictionary

Question Video Describing The Structure Of The Myelin Sheath Nagwa
Myelination Of Axons By Schwann Cells

Node Of Ranvier Anatomy Britannica

Describe The Basic Structure Of A Neuron Including The Axon Dendrites And Synapse Socratic Neurons Dendrite Human Body Systems

Myelin Sheath What They Are Their Function Damage Simply Psychology

Myelin Sheath What They Are Their Function Damage Simply Psychology
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/the-myelin-sheath-and-myelination/K80rK5rTyuEqP5dgdL6vpw_6cpqYHOG8uJ79tkTRT0c4w_schwann_cells_forming_the_myelin_sheath.png)
Myelin Sheath Myelination Function Clinical Relations Kenhub

Myelin Sheath What They Are Their Function Damage Simply Psychology

Structure Of Motor Neuron Vector Diagram Include Dendrites Cell Body With Nucleus Axon Myelin Sheath Nodes Of Ranvier Motor Neuron Neurons Neuron Diagram

Myelin Sheath What They Are Their Function Damage Simply Psychology
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/10996/anatomy-neurons-basic-types_english.jpg)
Myelin Sheath Myelination Function Clinical Relations Kenhub

Myelin Membrane Learn Science At Scitable

Myelin Biochemistry Britannica

Label The Parts Of A Neuron Neurons Cells Worksheet Teaching Biology



Comments
Post a Comment